Publication Date: 2024-08-13 | Regulator: European Banking Authority (EBA)
Title: Final Draft RTS on Fundamental Review of The Trading Book (FRTB)
Regulation Summary
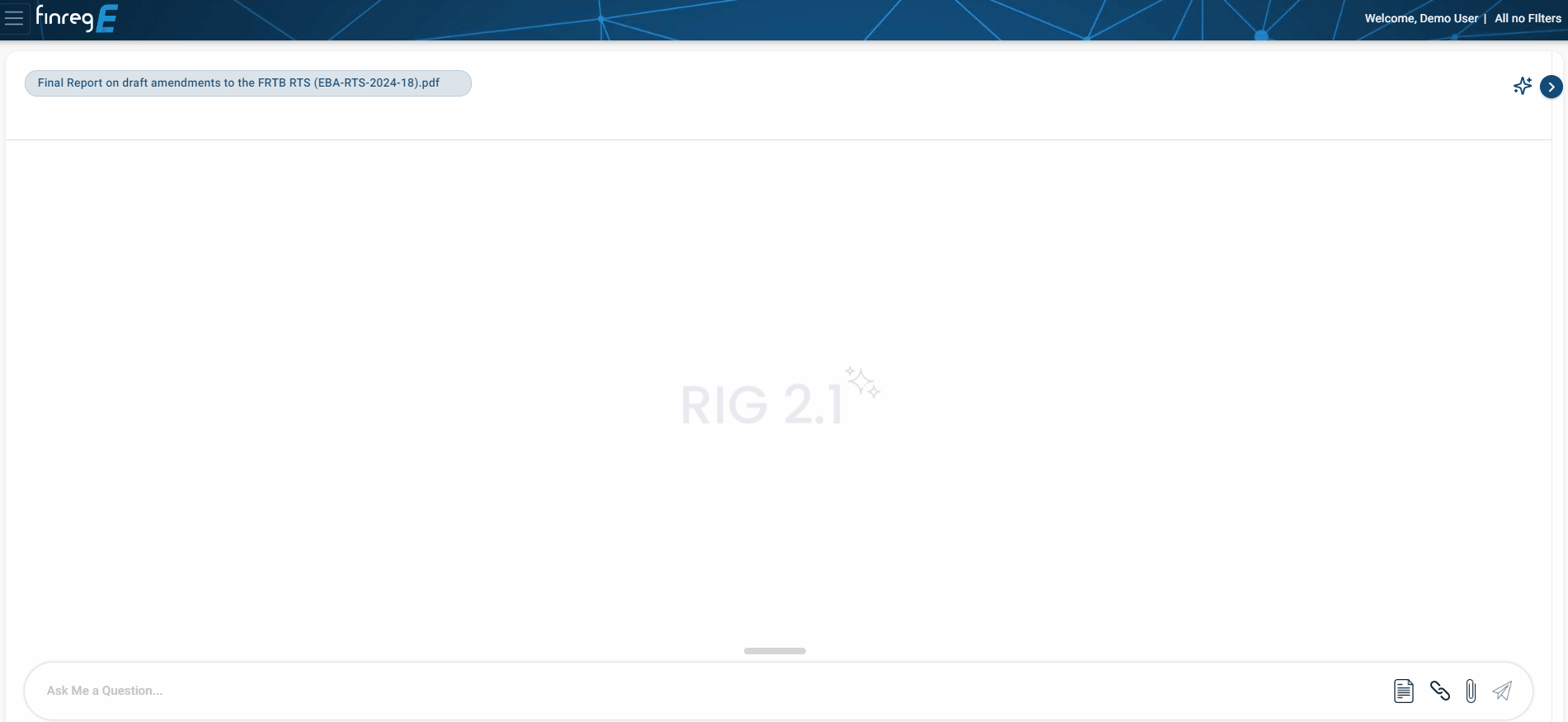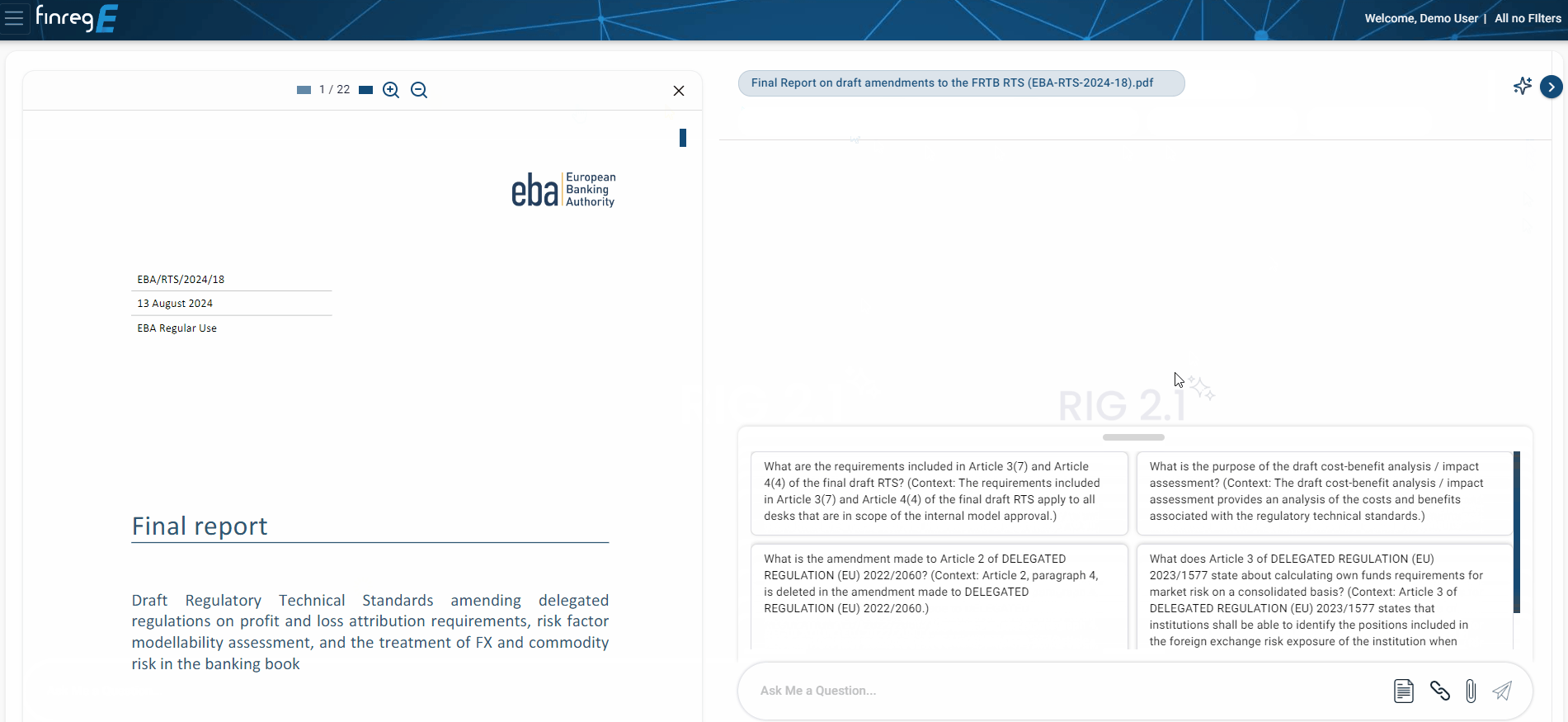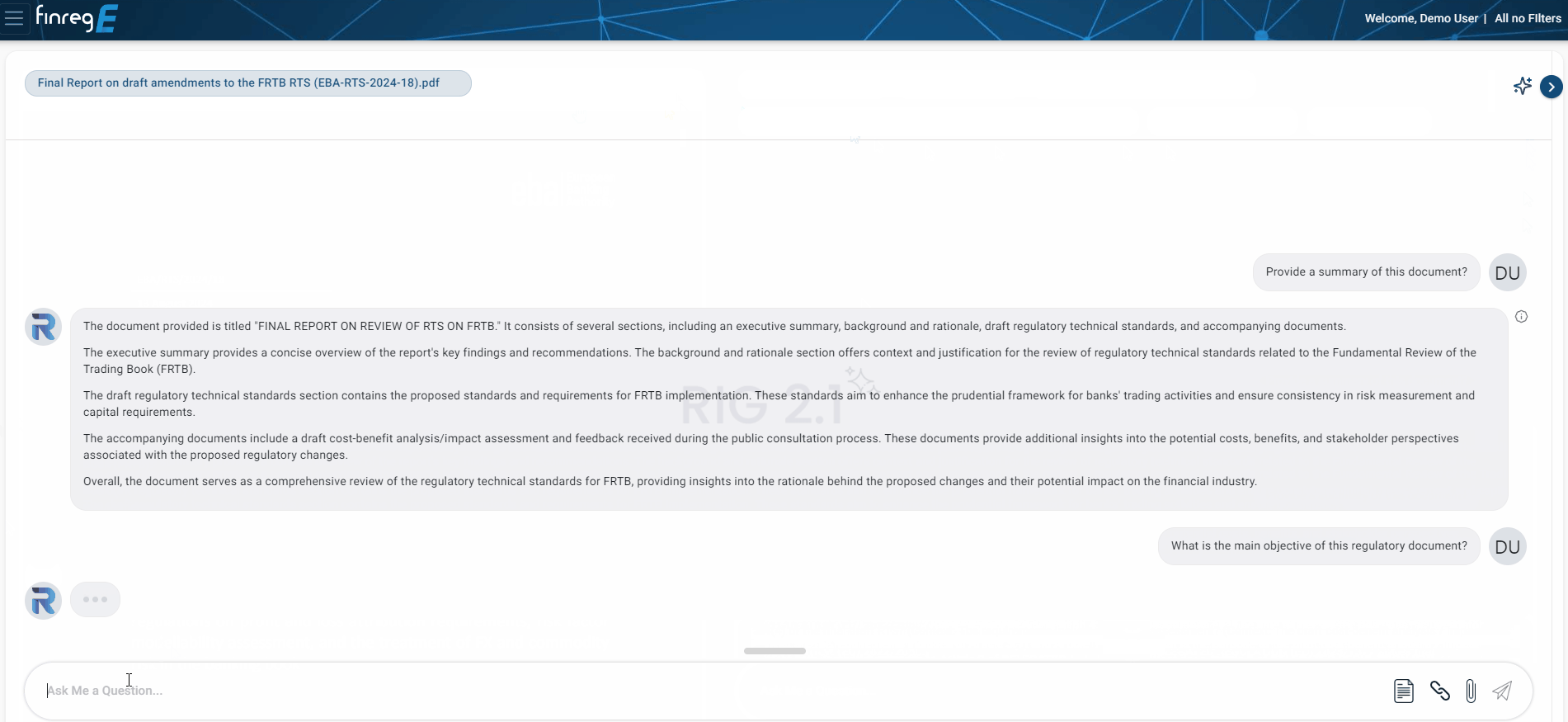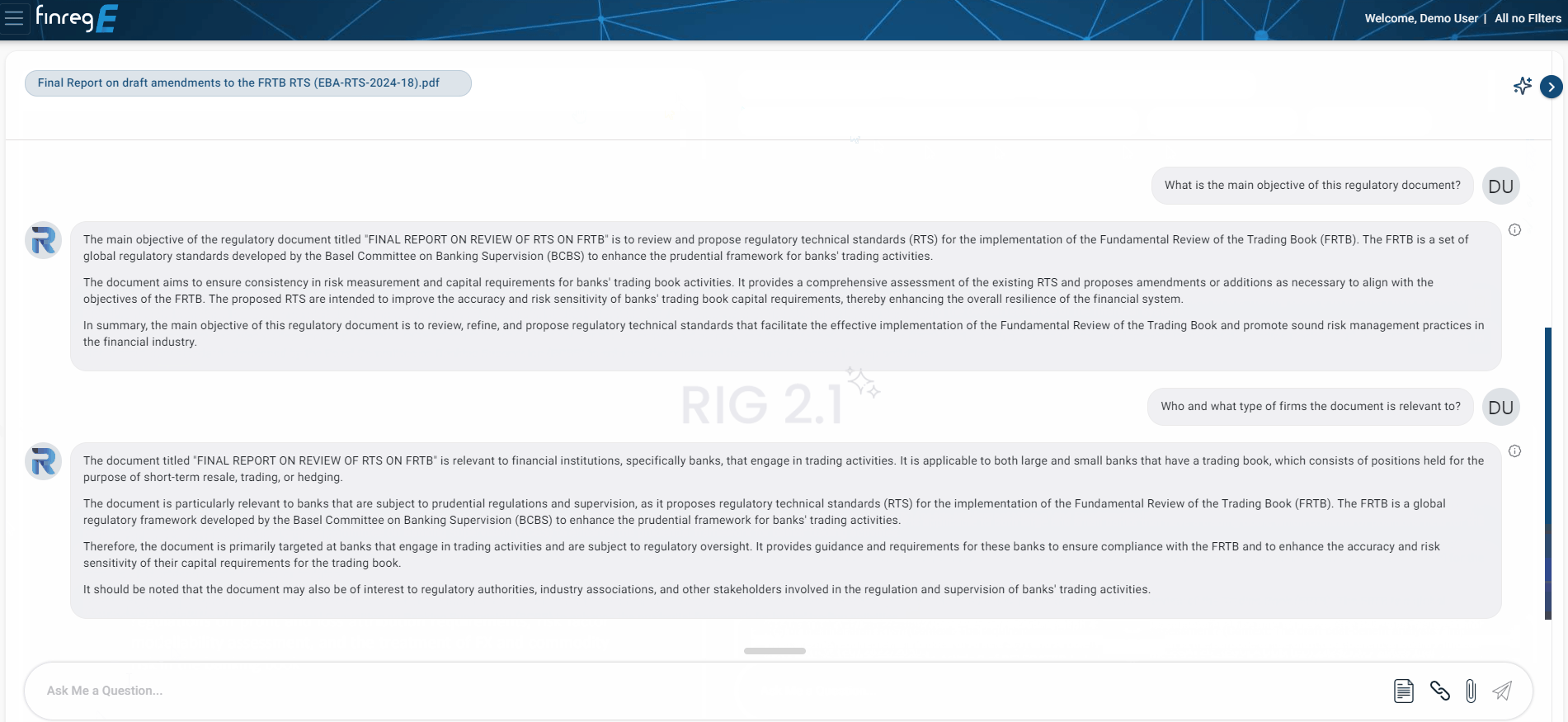
The document serves as a comprehensive review of the regulatory technical standards for FRTB, providing insights into the rationale behind the proposed changes and their potential impact on the financial industry.
The executive summary provides a concise overview of the report’s key findings and recommendations. The background and rationale section offers context and justification for the review of regulatory technical standards related to the Fundamental Review of the Trading Book (FRTB).
The draft regulatory technical standards section contains the proposed standards and requirements for FRTB implementation. These standards aim to enhance the prudential framework for banks’ trading activities and ensure consistency in risk measurement and capital requirements.
The accompanying documents include a draft cost-benefit analysis/impact assessment and feedback received during the public consultation process. These documents provide additional insights into the potential costs, benefits, and stakeholder perspectives associated with the proposed regulatory changes.
Questions we asked our AI Regulatory Insights Generator (RIG)
What is the main objective of this regulatory document?
The main objective of the regulatory document is to review and propose regulatory technical standards (RTS) for the implementation of the Fundamental Review of the Trading Book (FRTB). The FRTB is a set of global regulatory standards developed by the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision (BCBS) to enhance the prudential framework for banks’ trading activities.
The document aims to ensure consistency in risk measurement and capital requirements for banks’ trading book activities. It provides a comprehensive assessment of the existing RTS and proposes amendments or additions as necessary to align with the objectives of the FRTB. The proposed RTS are intended to improve the accuracy and risk sensitivity of banks’ trading book capital requirements, thereby enhancing the overall resilience of the financial system.
In summary, the main objective of this regulatory document is to review, refine, and propose regulatory technical standards that facilitate the effective implementation of the Fundamental Review of the Trading Book and promote sound risk management practices in the financial industry.
Who and what type of firms the document is relevant to?
The document is relevant to financial institutions, specifically banks, that engage in trading activities. It is applicable to both large and small banks that have a trading book, which consists of positions held for the purpose of short-term resale, trading, or hedging.
The document is particularly relevant to banks that are subject to prudential regulations and supervision, as it proposes regulatory technical standards (RTS) for the implementation of the Fundamental Review of the Trading Book (FRTB). The FRTB is a global regulatory framework developed by the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision (BCBS) to enhance the prudential framework for banks’ trading activities.
Therefore, the document is primarily targeted at banks that engage in trading activities and are subject to regulatory oversight. It provides guidance and requirements for these banks to ensure compliance with the FRTB and to enhance the accuracy and risk sensitivity of their capital requirements for the trading book.
It should be noted that the document may also be of interest to regulatory authorities, industry associations, and other stakeholders involved in the regulation and supervision of banks’ trading activities.
What impact will the amendments mentioned in the document have on financial institutions already complying with the existing RTS?
The amendments mentioned in the document will have several impacts on financial institutions that are already complying with the existing Regulatory Technical Standards (RTS). It is important for financial institutions already complying with the existing RTS to carefully review the amendments, assess their impact, and take necessary actions to ensure compliance with the revised requirements. This may involve updating internal policies, enhancing position identification processes, and aligning risk management practices with the expanded scope of applicability. Regular communication with regulators and industry associations can provide further guidance on the specific implications and implementation timelines.
Here are the key impacts:
- Expanded Scope of Applicability:
- The amendments clarify that certain requirements included in the RTS, such as trading desk requirements, apply not only to institutions using an internal model but also to those using the standardized approach.
- Financial institutions that were previously complying with the existing RTS using the standardized approach will now need to ensure compliance with the additional requirements applicable to trading desks.
- Review and Update Internal Policies:
- Financial institutions will need to review their internal policies to ensure they align with the amendments.
- This includes updating policies to address the expanded scope of applicability and incorporating the requirements related to position management by classical trading desks and notional trading desks.
- Enhanced Position Identification:
- The amendments introduce requirements to identify positions that are subject to foreign exchange (FX) risk solely due to translation risk resulting from the consolidation process.
- Financial institutions will need to enhance their processes and systems to accurately identify and manage such positions.
- Regulatory Stability and Predictability:
- The amendments aim to align the existing RTS with the changes introduced in the Capital Requirements Regulation (CRR3) framework.
- Financial institutions that have already implemented the existing RTS will need to make limited changes to align with the amendments in CRR3, ensuring regulatory stability and consistency in the framework.
- Compliance with Revised Requirements:
- Financial institutions will need to ensure compliance with the revised requirements introduced by the amendments.
- This may involve updating risk management practices, enhancing position management controls, and aligning internal processes with the new requirements.
What changes are being made to the Profit and Loss Attribution (PLAT) requirements in the FRTB framework?
According to the provided documents, the Profit and Loss Attribution (PLAT) requirements in the Fundamental Review of the Trading Book (FRTB) framework are being amended. The specific changes made to the PLAT requirements are outlined in Article 325bg of the Capital Requirements Regulation (CRR3). It is important for financial institutions to carefully review and understand these changes to the PLAT requirements to ensure compliance with the updated regulations and adjust their internal processes and risk management practices accordingly.
The amendments to the PLAT requirements can be summarized as follows:
- Clarification of PLAT requirements: The amendments clarify that if the hypothetical profit and loss (HPL) and risk-theoretical profit and loss (RTPL) are either close or sufficiently close, the PLAT requirements are considered met. In such cases, the desk is allowed to continue using the internal model approach for calculating own funds requirements for market risk. However, if the HPL and RTPL are not close or sufficiently close, the desk falls under the standardized approach as specified in Article 325az(2)(d) of the CRR3.
- Introduction of an add-on: The amendments introduce an add-on, referred to as PLAaddon, for desks where the HPL and RTPL are not close but are sufficiently close. This add-on is applied to the own funds’ requirements for market risk calculation.
- Classification of desks: The amendments classify desks into different categories based on the proximity of HPL and RTPL. Green and yellow desks, as allocated according to the rules prescribed in the delegated regulation on PLAT and back-testing requirements, are considered to have HPL and RTPL close or sufficiently close, thereby passing the PLAT requirements. On the other hand, amber and red desks are considered to have HPL and RTPL neither close nor sufficiently close, resulting in non-compliance with the PLAT requirements.
What changes are being made to the modellability assessment requirements in the FRTB framework?
The provided documents mention changes being made to the modellability assessment requirements in the Fundamental Review of the Trading Book (FRTB) framework. These changes are outlined in Article 325be of the Capital Requirements Regulation (CRR3). It is important for financial institutions to carefully review and understand these changes to the modellability assessment requirements. They should ensure compliance with the updated regulations by appropriately documenting the use of third-party market data and providing the necessary assessments to competent authorities. This will help facilitate the modellability assessment process and ensure adherence to the FRTB framework.
The specific changes made to the modellability assessment requirements can be summarized as follows:
- Use of third-party market data: The amendments make it more explicit that competent authorities may allow institutions to use market data provided by third-party vendors for the modellability assessment. This means that institutions can utilize data from external sources to assess the modellability of risk factors.
- Documentation requirements: The amendments introduce documentation requirements to support competent authorities in assessing the use of third-party market data. Institutions are required to provide an assessment of the number of risk factors for which data from a specific source has been used in the modellability assessment. This documentation helps demonstrate the reliance on third-party data and assists in the evaluation process by competent authorities.
What changes are being made to the FX and Commodity risk in the banking book requirements in the FRTB framework?
According to the provided documents, changes are being made to the requirements related to Foreign Exchange (FX) and Commodity risk in the banking book in the Fundamental Review of the Trading Book (FRTB) framework. These changes are outlined in Article 104b of the Capital Requirements Regulation (CRR3). It is important for financial institutions to carefully review and understand these changes to the FX and Commodity risk in the banking book requirements. They should ensure compliance with the updated regulations by appropriately assigning positions to trading desks, identifying translation risk, and establishing clear policies for internal model banks. This will help ensure effective risk management and adherence to the FRTB framework.
The specific changes made to the FX and Commodity risk in the banking book requirements can be summarized as follows:
- Assignment of positions to trading desks: Institutions are required to assign their non-trading book positions that are subject to FX risk or commodity risk to trading desks established in accordance with the regulations. This ensures that positions with similar risks are managed by the appropriate trading desks.
- Notional trading desks: Institutions have the option to establish one or more trading desks exclusively for non-trading book positions subject to FX risk or commodity risk. These notional trading desks are exempt from certain governance requirements applicable to classical trading desks.
- Identification of translation risk: The amendments introduce requirements to ensure that institutions can identify positions that are subject to FX risk solely due to translation risk resulting from the consolidation process. This helps distinguish positions affected by translation risk from other FX risk positions.
- Policy clarification for internal model banks: Institutions using internal models are required to have clear policies in place that specify which positions are managed by classical trading desks and which positions are managed within the context of a notional trading desk. This ensures transparency and clarity in the management of different types of positions.
Any additional information firms should pay attention to?
In addition to the specific changes mentioned earlier, there are a few additional points that financial institutions should pay attention to in relation to the FRTB framework. Financial institutions should ensure that they have a thorough understanding of these requirements and make any necessary adjustments to their systems, processes, and policies to comply with the updated regulations. Regular monitoring and review of compliance with the FRTB framework will be essential to maintain regulatory compliance and effective risk management.
The additional points are:
- Consolidated basis for market risk: Institutions should ensure that when calculating their own funds requirements for market risk on a consolidated basis, they can identify the positions included in the foreign exchange risk exposure resulting from the translation of positions into the reporting currency. This is important for accurate risk assessment and reporting.
- Internal risk-management systems: Institutions should have robust internal risk-management systems in place to identify and manage positions subject to foreign exchange risk. These systems should align with the requirements of Article 325b of the Capital Requirements Regulation (CRR3) and enable effective monitoring and control of foreign exchange risk exposure.
- Compliance with internal policies: Institutions must document whether non-trading book positions subject to foreign exchange risk are assigned to a trading desk managing exclusively non-trading book positions or to a trading desk managing both trading and non-trading book positions. This documentation should be part of the internal policies referred to in Article 325bi of the CRR3.
- Documentation of third-party vendors: If institutions use third-party vendors as sources of verifiable price information for modellability assessment, they should document the number of risk factors classified as modellable based on the prices provided by each vendor. Additionally, a materiality assessment of those risk factors should be conducted and documented.
We then asked the RIG to auto-generate a suggested control framework and write a policy
Suggest a control framework for the firms to comply with this regulation?
To comply with the regulations related to the Fundamental Review of the Trading Book (FRTB), financial firms should establish a comprehensive control framework. While the specific control framework may vary based on the firm’s size, complexity, and risk profile, I can provide a suggested framework that covers key areas of compliance. Firms should consult with their internal risk management teams, compliance officers, and legal advisors to develop a control framework that aligns with their unique circumstances and regulatory requirements.
Here is a suggested control framework:
Risk Governance and Policies:
- Establish a clear governance structure with defined roles and responsibilities for risk management.
- Develop and implement risk management policies and procedures that align with the FRTB requirements.
- Ensure regular review and approval of risk management policies by senior management and the board of directors.
Risk Identification and Assessment:
- Implement robust processes to identify, measure, and assess market risks associated with trading activities.
- Develop methodologies and models to accurately quantify market risks, including price risk, foreign exchange risk, and commodity risk.
- Conduct regular risk assessments to identify emerging risks and ensure risk exposures are within acceptable limits.
Internal Controls and Processes:
- Establish strong internal controls to monitor and mitigate market risks effectively.
- Implement pre-trade and post-trade controls to ensure compliance with risk limits and regulatory requirements.
- Conduct independent validation and testing of risk models and methodologies to ensure accuracy and reliability.
Capital Adequacy and Reporting:
- Develop processes to calculate and maintain sufficient own funds requirements for market risk.
- Establish robust reporting mechanisms to provide accurate and timely information to regulatory authorities.
- Ensure compliance with regulatory reporting requirements, including periodic reporting of capital adequacy ratios and risk exposures.
Documentation and Recordkeeping:
- Maintain comprehensive documentation of risk management processes, methodologies, and models.
- Establish a centralized repository for storing and managing risk-related documentation.
- Implement procedures for recordkeeping and retention in accordance with regulatory requirements.
Compliance Monitoring and Testing:
- Conduct regular compliance monitoring and testing to assess the effectiveness of risk management controls.
- Perform internal audits and assessments to identify control weaknesses and areas for improvement.
- Establish a process for addressing and remediating identified compliance issues.
Training and Awareness:
- Provide regular training and awareness programs to employees on risk management policies and procedures.
- Foster a culture of risk awareness and compliance throughout the organization.
- Ensure employees have the necessary skills and knowledge to effectively manage market risks.
Suggest a policy on risk management requirement based on this document?
Title: Risk Management Policy for FRTB Compliance
Objective
The objective of this policy is to establish a comprehensive risk management framework to ensure compliance with the regulatory requirements outlined in the RTS related to the Fundamental Review of the Trading Book (FRTB).
Scope
This policy applies to all trading activities and positions subject to market risk within the organization.
Risk Identification and Assessment
- Establish robust processes to identify, measure, and assess market risks associated with trading activities, including price risk, foreign exchange risk, and commodity risk.
- Develop methodologies and models to accurately quantify market risks, ensuring compliance with the FRTB requirements.
- Conduct regular risk assessments to identify emerging risks and ensure risk exposures are within acceptable limits.
Risk Governance and Policies
- Establish a clear governance structure with defined roles and responsibilities for risk management.
- Develop and implement risk management policies and procedures that align with the FRTB requirements.
- Ensure regular review and approval of risk management policies by senior management and the board of directors.
Internal Controls and Processes
- Implement pre-trade and post-trade controls to ensure compliance with risk limits and regulatory requirements.
- Establish strong internal controls to monitor and mitigate market risks effectively.
- Conduct independent validation and testing of risk models and methodologies to ensure accuracy and reliability.
Capital Adequacy and Reporting
- Develop processes to calculate and maintain sufficient own funds requirements for market risk in accordance with the FRTB regulations.
- Establish robust reporting mechanisms to provide accurate and timely information to regulatory authorities.
- Ensure compliance with regulatory reporting requirements, including periodic reporting of capital adequacy ratios and risk exposures.
Documentation and Recordkeeping
- Maintain comprehensive documentation of risk management processes, methodologies, and models.
- Establish a centralized repository for storing and managing risk-related documentation.
- Implement procedures for recordkeeping and retention in accordance with regulatory requirements.
Compliance Monitoring and Testing
- Conduct regular compliance monitoring and testing to assess the effectiveness of risk management controls.
- Perform internal audits and assessments to identify control weaknesses and areas for improvement.
- Establish a process for addressing and remediating identified compliance issues.
Training and Awareness
- Provide regular training and awareness programs to employees on risk management policies and procedures.
- Foster a culture of risk awareness and compliance throughout the organization.
- Ensure employees have the necessary skills and knowledge to effectively manage market risks.
Policy Review
This policy will be reviewed periodically to ensure its continued relevance and effectiveness in meeting regulatory requirements and addressing emerging risks.
Please note that this suggested policy is a starting point and should be customized to align with your firm’s specific risk management framework, regulatory requirements, and internal processes. It is recommended to involve relevant stakeholders, such as risk management, compliance, and legal teams, in the development and review of this policy to ensure its suitability and effectiveness for your organization.
By automatically interpreting regulatory documents and providing actionable insights, our platform ensures that your organization remains compliant with the latest amendments. To experience how FinregE can transform your compliance processes, book a demo today and see our AI RIG in action.