In the labyrinthine world of regulatory compliance, financial institutions grapple with a never-ending challenge – translating complex regulatory rules into practical, actionable compliance procedures and policies. The sheer volume of regulatory texts makes this task a Herculean endeavour. Fortunately, advancements in technology have brought a powerful ally to the forefront: Natural Language Processing (NLP) and text analytics.
Regulatory Obligation Mapping?

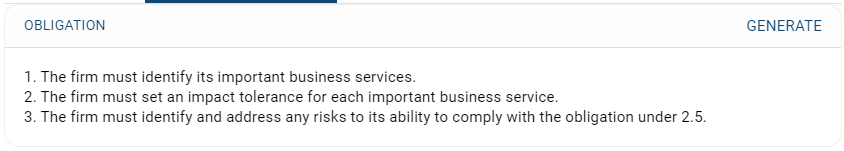
Figure 1: Example of regulatory obligations for PRA’s rules on Operational Resilience identified by FinregE’s RIG (Regulatory Insights Generator)
Before we delve into the transformative potential of NLP and text analytics, let’s grasp the significance of regulatory obligations in compliance. These obligations represent the specific actions and requirements imposed by regulatory authorities. Understanding them is the key to compliance, yet they are often buried in vast volumes of regulatory documents.
This is where NLP and text analytics step in.
How is NLP essential in this context?
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is a field of artificial intelligence that focuses on the interaction between computers and human language. In the realm of regulatory compliance, it serves as a bridge between the complex language of regulations and can help create the actionable insights required by financial institutions if leveraged correctly.
Market participants are inundated with regulatory documents, ranging from regulations and legislation themselves to lengthy news serving regulatory changes and proposals to how existing regulations will change/new laws will be introduced. Deciphering these texts manually is not only extremely time-consuming and error-prone, it´s very costly, too. NLP automates this process, extracting obligations and actions from regulatory texts with remarkable precision. And at rapid speeds.
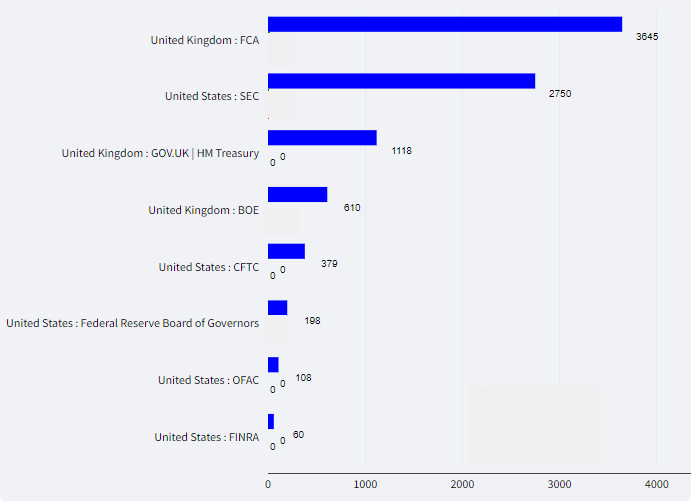
Figure 2: FinregE’s regulatory change viewer captured nearly 10,000 regulatory publications across major financial services regulators
The Power of Text Analytics
Complementing NLP, text analytics plays a crucial role in making sense of regulatory documents. Text analytics refers to the process of extracting meaningful information and patterns from unstructured text data. In the context of compliance, it helps in categorizing, structuring, and analyzing the content of regulatory documents.
The magnitude of regulations an organisation has to deal with – laws, regulations, compliance guidelines- is ever increasing. Text analytics simplifies large-scale data processing

Figure 3: Number of rules across key US and UK regulator
Bridging the Gap: Translating Rules to Actions
NLP and text analytics work in tandem to extract obligations from regulatory texts. They break down complex sentences, identify requirements, and structure the information in a way that makes it usable.
NLP and text analytics work in tandem to extract obligations from regulatory texts. They break down complex sentences, identify requirements, and structure the information in a way that makes it usable.
This ensures that technology adopters can be much quicker identifying and acting upon obligations imposed by regulators.
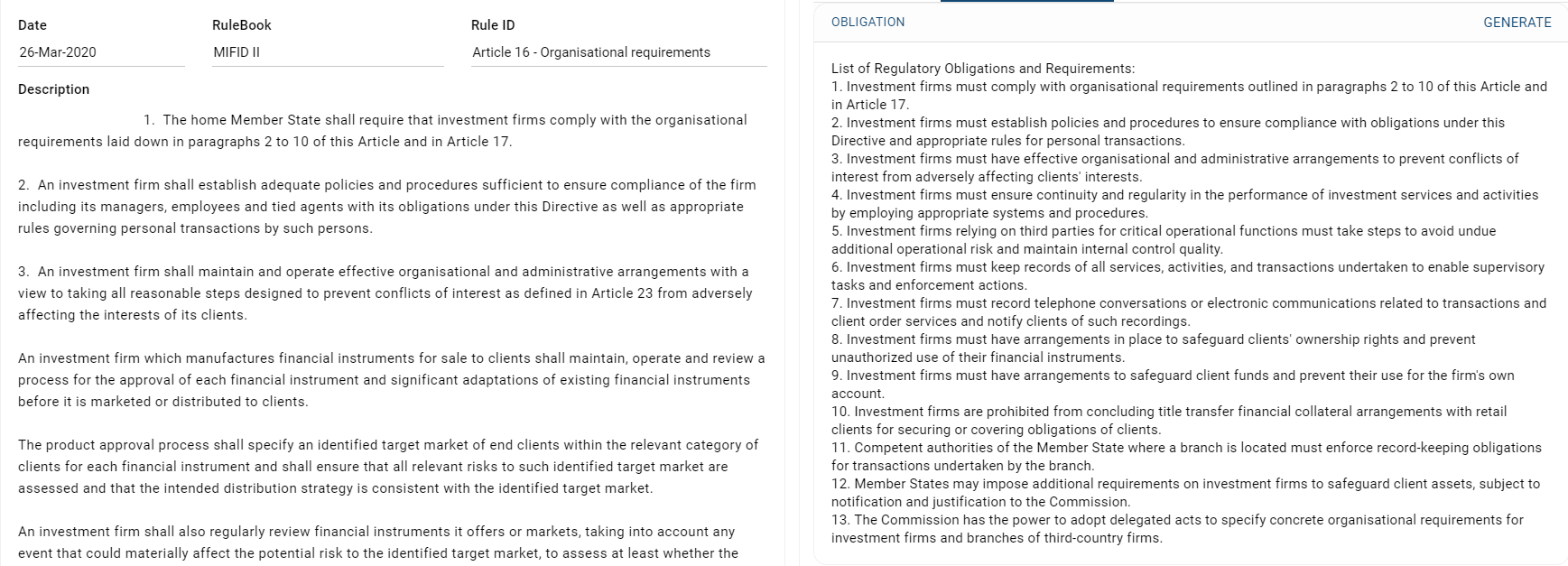
Figure 4: FinregE’s RIG generated regulatory obligations for MiFIDII Article 16 on Organisational Requirements
Real-World Applications
Users report faster and more accurate obligation extraction, enabling them to respond promptly to regulatory changes.
Overcoming Compliance Challenges
The sheer volume of regulatory documents, language barriers, and the dynamic nature of regulations create roadblocks. NLP plays a vital role in overcoming these challenges.
By automating the extraction of obligations, NLP eliminates the downsides of manual text analysis. It ensures that nothing slips through the cracks, keeping institutions in compliance.
Regulatory Obligation Mapping with FinregE
FinregE´s platform empowers institutions to extract, map, and organize regulatory obligations effortlessly. It streamlines the compliance process by providing a structured repository of rules, obligations, and associated internal procedures and policies.
Maintain an organized and fully mapped digital library, makes it easier to search for and adapt regulatory compliance for reporting and change purposes.
FinregE’s users report faster and more accurate obligation extraction, enabling them to respond promptly to regulatory changes.
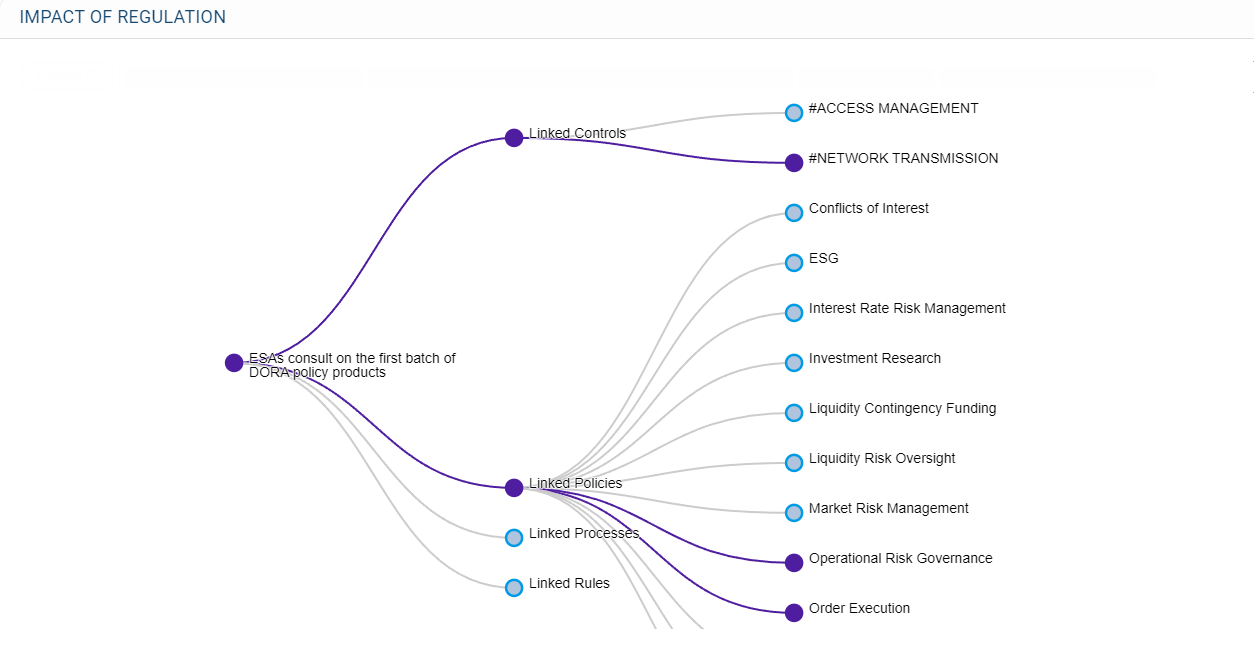
Figure 5: Mapping in FinregE of regulatory obligations to policies, risks and controls
Enhancing Compliance Procedures and Policies
The extracted obligations are not just data points. They are the foundation for structuring compliance procedures and policies. When financial institutions work with FinregE’s ML/NLP driven obligations, they can produce compliance documents linked directly to the actions required under regulatory rules.
The result? Clarity and precision in compliance documents, which in turn means that employees and stakeholders can easily understand their responsibilities and adhere to them, whilst reducing risks of compliance violations simultaneously.
Measuring Success
To evaluate the effectiveness of ML/NLP in compliance, institutions look at the time saved, reduction in errors, and increased accuracy in obligation extraction. Ultimately, success in compliance is about meeting regulatory requirements efficiently and accurately.
Financial institutions can also assess their compliance outcomes. Are they better equipped to adapt to regulatory changes? Are compliance policies and procedures clearer and more actionable? These metrics paint a clear picture of the value brought by NLP in regulatory obligation mapping.
Conclusion
In a world of complex regulatory landscapes, NLP and text analytics offer a way out of the maze. They transform regulatory rules from intimidating texts into ready-to-go compliance procedures and policies. Technology users that harness this power are there for much better equipped to navigate the ever-changing compliance landscape with efficiency and precision.
In a nutshell, NLP is not just about processing language; it’s about converting words into actions, ensuring that organisations remain compliant, by paving the way for a more organized, efficient, and future-proofed compliance process.